hdu6567 Cotree (树形dp 树的重心)
本文共 1711 字,大约阅读时间需要 5 分钟。
Problem Description
Avin has two trees which are not connected. He asks you to add an edge between them to make them connected while minimizing the function
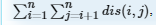 , where dis(i,j) represents the number of edges of the path from i to j. He is happy with only the function value.
, where dis(i,j) represents the number of edges of the path from i to j. He is happy with only the function value. Input
The first line contains a number n (2<=n<=100000). In each of the following n−2 lines, there are two numbers u and v, meaning that there is an edge between u and v. The input is guaranteed to contain exactly two trees.
Output
Just print the minimum function value.
Sample Input
3
1 2Sample Output
4
思路:
树中所有点到某个点的距离和中,到重心的距离和是最小的;
如果有两个重心,那么他们的距离和一样两次dfs树形dp找到两颗树的重心
把两个重心连接起来 再dfs树形dp一次计算答案计算树上任意两点的距离和,转化为计算每条边被经过的次数乘上边权
每条边被经过的次数等于这条边分隔开的 两端点分别所在的连通块的大小相乘 最后一次dfs树形dp的过程中 假设u是v的父节点, 以v为根的子树大小为sz[v] 则连接他们的边被经过的次数为(n-sz[v])*sz[v]code:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std;#define ll long longconst int inf=1e9;const int maxm=1e5+5;int head[maxm],nt[maxm<<1],to[maxm<<1],cnt;int mark[maxm];int sz[maxm],son[maxm];int num;//第一个连通块的大小int size;//第二个连通块的大小int root1,root2;int n;ll ans;void init(){ memset(head,0,sizeof head); memset(mark,0,sizeof mark); cnt=1; num=0; ans=0;}void add(int x,int y){ cnt++;nt[cnt]=head[x];head[x]=cnt;to[cnt]=y;}void dfs(int x){ num++;//计算连通块大小 sz[x]=1; son[x]=0; mark[x]=1; for(int i=head[x];i;i=nt[i]){ int v=to[i]; if(mark[v])continue; dfs(v); sz[x]+=sz[v]; son[x]=max(son[x],sz[v]); }}void dfs2(int x){ sz[x]=1; son[x]=0; mark[x]=1; for(int i=head[x];i;i=nt[i]){ int v=to[i]; if(mark[v])continue; dfs2(v); sz[x]+=sz[v]; son[x]=max(son[x],sz[v]); } son[x]=max(son[x],size-sz[x]); if(son[x]
转载地址:http://bnzv.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
MySQL事务及其特性与锁机制
查看>>
mysql事务理解
查看>>
MySQL事务详解结合MVCC机制的理解
查看>>
MySQL事务隔离级别:读未提交、读已提交、可重复读和串行
查看>>
MySQL事务隔离级别:读未提交、读已提交、可重复读和串行
查看>>
webpack css文件处理
查看>>
mysql二进制包安装和遇到的问题
查看>>
MySql二进制日志的应用及恢復
查看>>
mysql互换表中两列数据方法
查看>>
mysql五补充部分:SQL逻辑查询语句执行顺序
查看>>
mysql交互式连接&非交互式连接
查看>>
MySQL什么情况下会导致索引失效
查看>>
Mysql什么时候建索引
查看>>
MySql从入门到精通
查看>>
MYSQL从入门到精通(一)
查看>>
MYSQL从入门到精通(二)
查看>>
mysql以下日期函数正确的_mysql 日期函数
查看>>
mysql以服务方式运行
查看>>
mysql优化--索引原理
查看>>
MySQL优化之BTree索引使用规则
查看>>